|
15-meter Band
The 15-meter band (also called the 21-MHz band or 15 meters) is an amateur radio frequency band spanning the shortwave spectrum from 21 to 21.45 MHz. The band is suitable for amateur long-distance communications, and such use is permitted in nearly all countries. Because 15-meter waves propagate primarily via reflection off of the F-2 layer of the ionosphere, the band is most useful for intercontinental communication during daylight hours, especially in years close to solar maxima, but the band permits long-distance without high-power station equipment outside such ideal windows. The 15-meter wavelength is harmonically related to that of the 40-meter band, so it is often possible to use an antenna designed for 40 meters. History The 15-meter band was designated by the 1947 International Radio Conference of Atlantic City in part to compensate for the loss of the 160-meter band to amateurs by the introduction of LORAN during World War II. The 15-meter band opened to amat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amateur Radio
Amateur radio, also known as ham radio, is the use of the radio frequency spectrum for purposes of non-commercial exchange of messages, wireless experimentation, self-training, private recreation, radiosport, contesting, and emergency communications. The term "amateur" is used to specify "a duly authorised person interested in radioelectric practice with a purely personal aim and without pecuniary interest;" (either direct monetary or other similar reward) and to differentiate it from commercial broadcasting, public safety (such as police and fire), or professional two-way radio services (such as maritime, aviation, taxis, etc.). The amateur radio service (''amateur service'' and '' amateur-satellite service'') is established by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) through the Radio Regulations. National governments regulate technical and operational characteristics of transmissions and issue individual station licenses with a unique identifying call sign, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shortwave
Shortwave radio is radio transmission using shortwave (SW) radio frequencies. There is no official definition of the band, but the range always includes all of the high frequency band (HF), which extends from 3 to 30 MHz (100 to 10 metres); above the medium frequency band (MF), to the bottom of the VHF band. Radio waves in the shortwave band can be reflected or refracted from a layer of electrically charged atoms in the atmosphere called the ionosphere. Therefore, short waves directed at an angle into the sky can be reflected back to Earth at great distances, beyond the horizon. This is called skywave or "skip" propagation. Thus shortwave radio can be used for communication over very long distances, in contrast to radio waves of higher frequency, which travel in straight lines (line-of-sight propagation) and are limited by the visual horizon, about 64 km (40 miles). Shortwave broadcasts of radio programs played an important role in the early days of radio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DXing
DXing is the hobby of receiving and identifying distant radio or television signals, or making two-way radio contact with distant stations in amateur radio, citizens' band radio or other two-way radio communications. Many DXers also attempt to obtain written verifications of reception or contact, sometimes referred to as " QSLs" or "veries". The name of the hobby comes from DX, telegraphic shorthand for "distance" or "distant". The practice of DXing arose during the early days of radio broadcasting. Listeners would mail "reception reports" to radio broadcasting stations in hopes of getting a written acknowledgement or a QSL card that served to officially verify they had heard a distant station. Collecting these cards became popular with radio listeners in the 1920s and 1930s, and reception reports were often used by early broadcasters to gauge the effectiveness of their transmissions. Although international shortwave broadcasts are on the decline, DXing remains popular among de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionosphere
The ionosphere () is the ionized part of the upper atmosphere of Earth, from about to above sea level, a region that includes the thermosphere and parts of the mesosphere and exosphere. The ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation. It plays an important role in atmospheric electricity and forms the inner edge of the magnetosphere. It has practical importance because, among other functions, it influences radio propagation to distant places on Earth. History of discovery As early as 1839, the German mathematician and physicist Carl Friedrich Gauss postulated that an electrically conducting region of the atmosphere could account for observed variations of Earth's magnetic field. Sixty years later, Guglielmo Marconi received the first trans-Atlantic radio signal on December 12, 1901, in St. John's, Newfoundland (now in Canada) using a kite-supported antenna for reception. The transmitting station in Poldhu, Cornwall, used a spark-gap transmitter to produce a signal with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
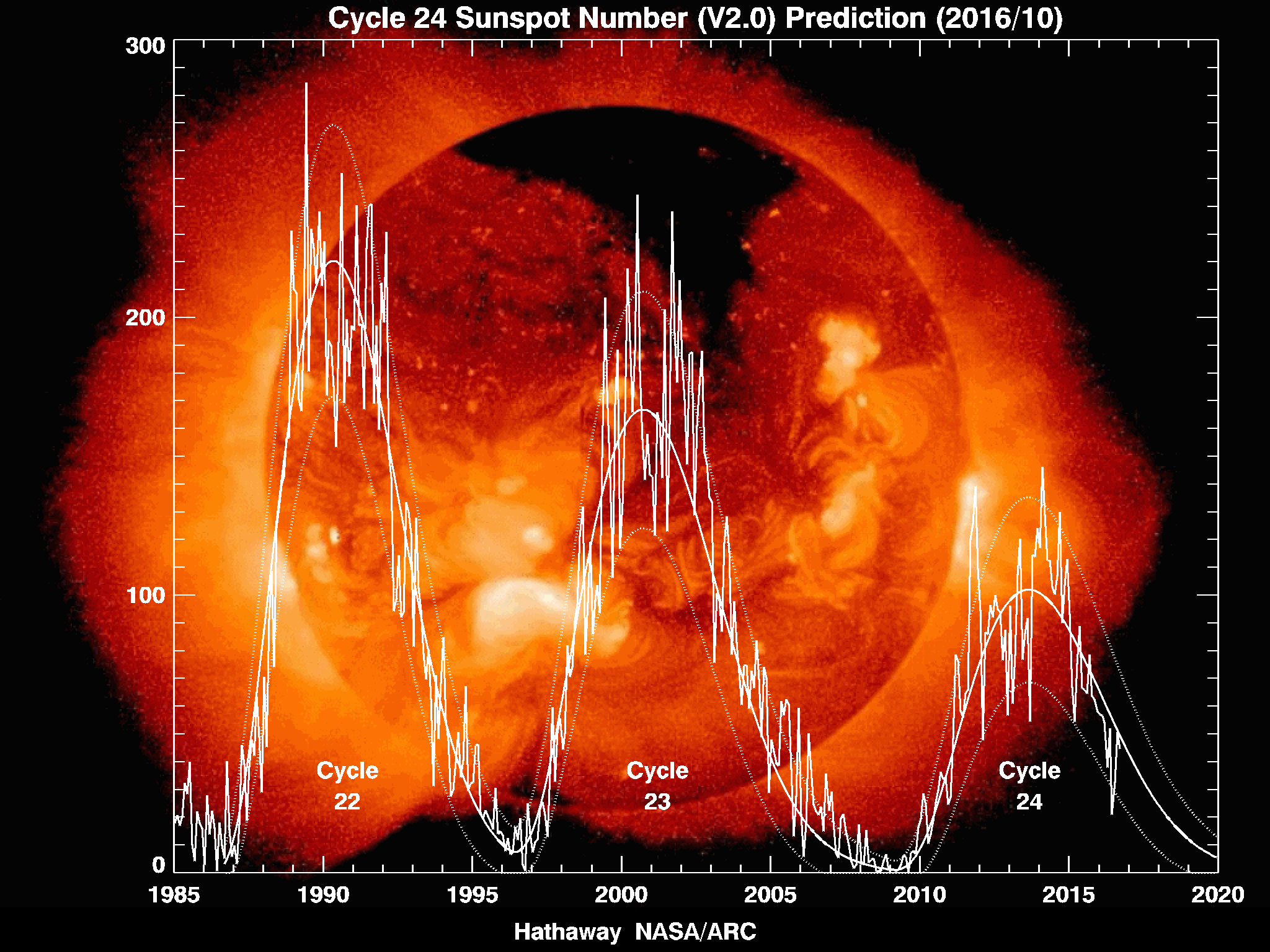
Solar Maxima
Solar maximum is the regular period of greatest solar activity during the Sun's 11-year solar cycle. During solar maximum, large numbers of sunspots appear, and the solar irradiance output grows by about 0.07%. On average, the solar cycle takes about 11 years to go from one solar maximum to the next, with duration observed varying from 9 to 14 years. Large solar storms often occur during solar maximum. For example, the Carrington Event, which took place a few months before the solar maximum of solar cycle 10, was the most intense geomagnetic storm in recorded history and widely considered to have been caused by an equally large solar storm. Predictions Predictions of a future maximum's timing and strength are very difficult; predictions vary widely. There was a solar maximum in 2000. In 2006, NASA initially expected a solar maximum in 2010 or 2011, and thought that it could be the strongest since 1958. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmonic
A harmonic is a wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the ''fundamental frequency'', the frequency of the original periodic signal, such as a sinusoidal wave. The original signal is also called the ''1st harmonic'', the other harmonics are known as ''higher harmonics''. As all harmonics are periodic at the fundamental frequency, the sum of harmonics is also periodic at that frequency. The set of harmonics forms a '' harmonic series''. The term is employed in various disciplines, including music, physics, acoustics, electronic power transmission, radio technology, and other fields. For example, if the fundamental frequency is 50 Hz, a common AC power supply frequency, the frequencies of the first three higher harmonics are 100 Hz (2nd harmonic), 150 Hz (3rd harmonic), 200 Hz (4th harmonic) and any addition of waves with these frequencies is periodic at 50 Hz. In music, harmonics are used on string instruments and wind ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
40-meter Band
The 40-meter or 7-MHz band is an amateur radio frequency band, spanning 7.000-7.300 MHz in ITU Region 2, and 7.000-7.200 MHz in Regions 1 & 3. It is allocated to radio amateurs worldwide on a primary basis; however, only 7.000-7.100 MHz is exclusively allocated to amateur radio worldwide. Shortwave broadcasters and land mobile users also have primary allocations in some countries, and amateur stations must share the band with these users. 40 meters is considered one of the most reliable all-season long distance communication ( DX) bands. History The 40-meter band was made available to amateurs in the United States by the Third National Radio Conference on October 10, 1924, ''Recommendations for Regulation of Radio Adopted by the Third National Radio Confere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antenna (radio)
In radio engineering, an antenna or aerial is the interface between radio waves propagating through space and electric currents moving in metal conductors, used with a transmitter or receiver (radio), receiver. In Transmission (telecommunications), transmission, a radio transmitter supplies an electric current to the antenna's terminals, and the antenna radiates the energy from the current as electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic waves (radio waves). In Receiver (radio), reception, an antenna intercepts some of the power of a radio wave in order to produce an electric current at its terminals, that is applied to a receiver to be Amplifier, amplified. Antennas are essential components of all radio equipment. An antenna is an array of conductor (material), conductors (Driven element, elements), electrically connected to the receiver or transmitter. Antennas can be designed to transmit and receive radio waves in all horizontal directions equally (omnidirectional antennas), o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LORAN
LORAN, short for long range navigation, was a hyperbolic radio navigation system developed in the United States during World War II. It was similar to the UK's Gee system but operated at lower frequencies in order to provide an improved range up to with an accuracy of tens of miles. It was first used for ship convoys crossing the Atlantic Ocean, and then by long-range patrol aircraft, but found its main use on the ships and aircraft operating in the Pacific theater during World War II. LORAN, in its original form, was an expensive system to implement, requiring a cathode ray tube (CRT) display. This limited use to the military and large commercial users. Automated receivers became available in the 1950s, but the same improved electronics also opened the possibility of new systems with higher accuracy. The U.S. Navy began development of Loran-B, which offered accuracy on the order of a few tens of feet, but ran into significant technical problems. The U.S. Air Force worked on a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuous Wave
A continuous wave or continuous waveform (CW) is an electromagnetic wave of constant amplitude and frequency, typically a sine wave, that for mathematical analysis is considered to be of infinite duration. It may refer to e.g. a laser or particle accelerator having a continuous output, as opposed to a pulsed output. Continuous wave is also the name given to an early method of radio transmission, in which a sinusoidal carrier wave is switched on and off. Information is carried in the varying duration of the on and off periods of the signal, for example by Morse code in early radio. In early wireless telegraphy radio transmission, CW waves were also known as "undamped waves", to distinguish this method from damped wave signals produced by earlier ''spark gap'' type transmitters. Radio Transmissions before CW Very early radio transmitters used a spark gap to produce radio-frequency oscillations in the transmitting antenna. The signals produced by these spark-gap transmitt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioteletype
Radioteletype (RTTY) is a telecommunications system consisting originally of two or more electromechanical teleprinters in different locations connected by radio rather than a wired link. Radioteletype evolved from earlier landline teleprinter operations that began in the mid-1800s. The US Navy Department successfully tested printing telegraphy between an airplane and ground radio station in 1922. Later that year, the Radio Corporation of America successfully tested printing telegraphy via their Chatham, Massachusetts, radio station to the R.M.S. Majestic. Commercial RTTY systems were in active service between San Francisco and Honolulu as early as April 1932 and between San Francisco and New York City by 1934. The US military used radioteletype in the 1930s and expanded this usage during World War II. From the 1980s, teleprinters were replaced by personal computers (PCs) running software to emulate teleprinters. The term radioteletype is used to describe both the original radi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Amateurs Of Canada
Radio Amateurs of Canada (RAC), known in French as Radio Amateurs du Canada, is the national association for Amateur Radio in Canada. It is a not-for-profit membership association with headquarters in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, representing the interests of Amateur Radio all across Canada. Speaking on behalf of Canadian Radio Amateurs, RAC provides liaison with government agencies and carries the Amateur voice about regulatory and spectrum issues to the discussion table with government and industry leaders, nationally and internationally. RAC is the Canadian voting member society of the International Amateur Radio Union. RAC also provides many services, publications and supplies to its members to enhance their enjoyment of Amateur Radio. The organization publishes a bimonthly magazine distributed to members called ''The Canadian Amateur''. History * 1967 — Canadian Amateur Radio Federation (CARF) formed * 1979 — Canadian Radio Relay League (CRRL) formed out of the Canadia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |