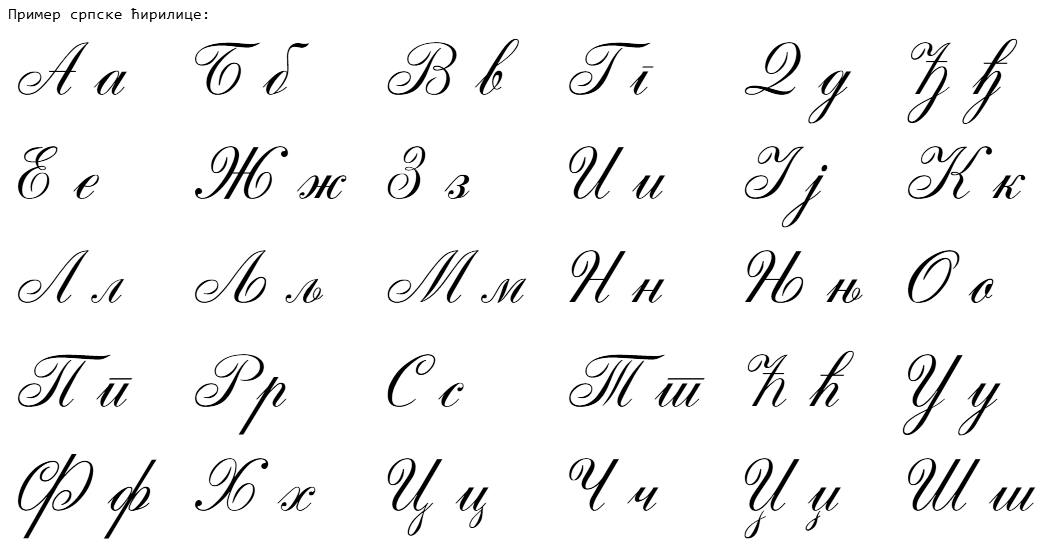|
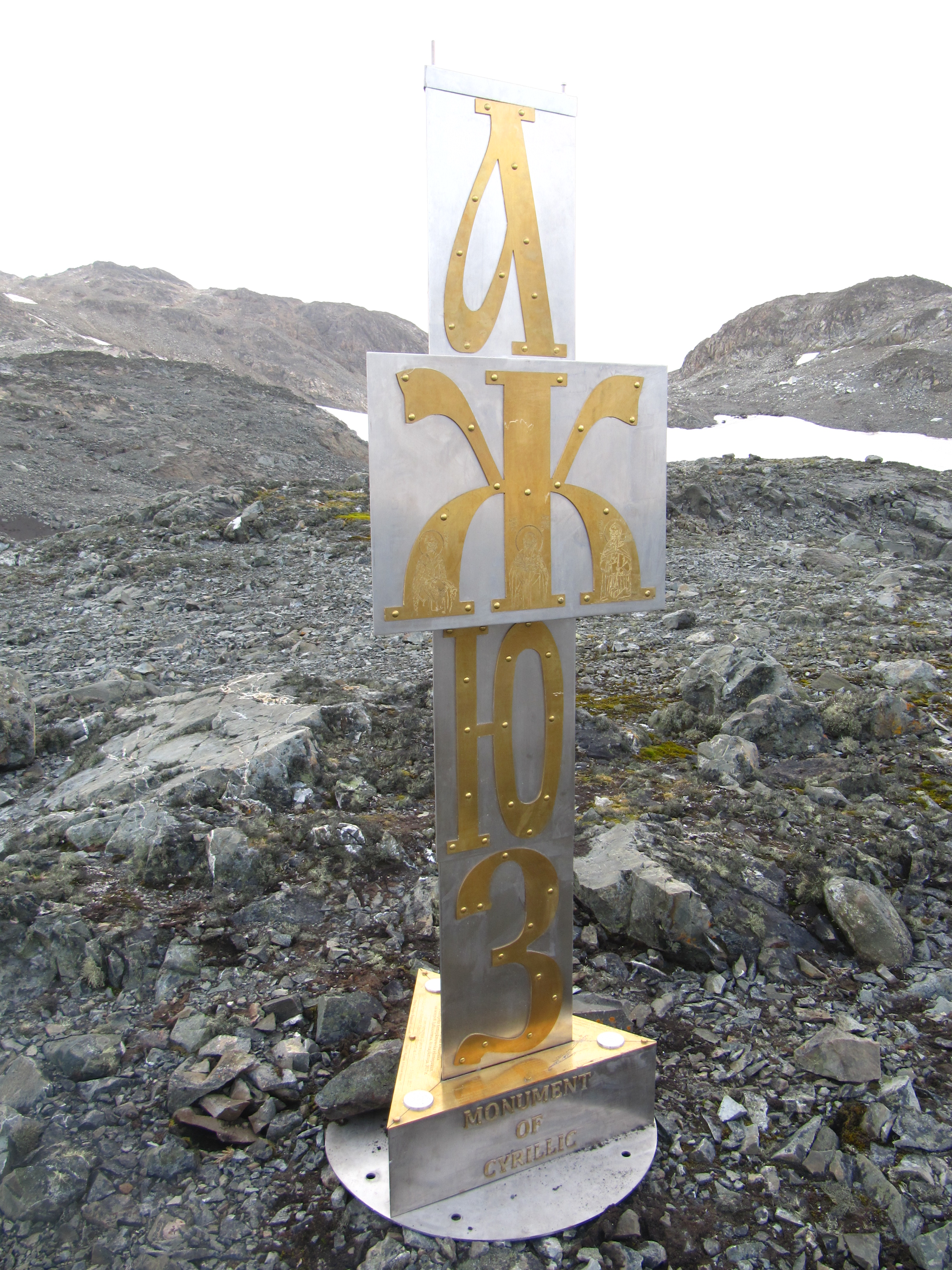
Cyrillic Script
The Cyrillic script ( ), Slavonic script or the Slavic script, is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Eastern Europe, the Caucasus, Central Asia, North Asia, and East Asia. , around 250 million people in Eurasia use Cyrillic as the official script for their national languages, with Russia accounting for about half of them. With the accession of Bulgaria to the European Union on 1 January 2007, Cyrillic became the third official script of the European Union, following the Latin and Greek alphabets. The Early Cyrillic alphabet was developed during the 9th century AD at the Preslav Literary School in the First Bulgarian Empire during the reign of tsar Simeon I the Great, probably by disciples of the two Byzantine brothers Saint Cyril and Saint Methodius, who had previously created the Glagolitic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Alphabet
The Russian alphabet (russian: ру́сский алфави́т, russkiy alfavit, , label=none, or russian: ру́сская а́збука, russkaya azbuka, label=none, more traditionally) is the script used to write the Russian language. It comes from the Cyrillic script, which was devised in the 9th century for the first Slavic literary language, Old Slavonic. Initially an old variant of the Bulgarian alphabet, it became used in the Kievan Rusʹ since the 10th century to write what would become the Russian language. The modern Russian alphabet consists of 33 letters: twenty consonants (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , ), ten vowels (, , , , , , , , , ), a semivowel / consonant (), and two modifier letters or "signs" (, ) that alter pronunciation of a preceding consonant or a following vowel. Letters : An alternative form of the letter El () closely resembles the Greek letter lambda (). Historic letters Letters eliminated in 1917–18 * — Id ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fita
Fita (Ѳ ѳ; italics: ) is a letter of the Early Cyrillic alphabet. The shape and the name of the letter are derived from the Greek letter theta (Θ θ). In the ISO 9 system, Ѳ is romanized using F grave accent (F̀ f̀). In the Cyrillic numeral system, Fita has a value of 9. Shape In traditional (Church Slavonic) typefaces, the central line is typically about twice the width of the letter's body and has serifs similar to those on the letter Т: . Sometimes the line is drawn as low as the baseline, which makes the letter difficult to distinguish from Д. Usage Old Russian and Church Slavonic The traditional Russian name of the letter is ''fitá'' (or, in pre-1918 spelling, ѳита́). Fita was mainly used to write proper names and loanwords derived from or via Greek. Russians pronounced these names with the sound instead of (like the pronunciation of in "thin"), for example "Theodore" was pronounced as "Feodor" (now "Fyodor"). Early texts in Russian ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukrainian Alphabet
The Ukrainian alphabet ( uk, абе́тка, áзбука алфа́ві́т, abetka, azbuka alfavit) is the set of letters used to write Ukrainian, which is the official language of Ukraine. It is one of several national variations of the Cyrillic script. It comes from the Cyrillic script, which was devised in the 9th century for the first Slavic literary language, called Old Slavonic. Since the 10th century, it became used in the Kyivan Rus' for Old East Slavic, from which the Belarusian, Russian, Rusyn, and Ukrainian alphabets later evolved. The modern Ukrainian alphabet has 33 letters in total: 20 consonants, 2 semivowels, 10 vowels and 1 palatalization sign. Sometimes the apostrophe (') is also included, which has a phonetic meaning and is a mandatory sign in writing, but is not considered as a letter and is not included in the alphabet. In Ukrainian, it is called (; tr. ''ukrayins'ka abetka''), from the initial letters '' а'' (tr. ''a'') and '' б'' (tr. ''b'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbian Alphabet
The Serbian Cyrillic alphabet ( sr, / , ) is a variation of the Cyrillic script used to write the Serbian language, updated in 1818 by Serbian linguist Vuk Karadžić. It is one of the two alphabets used to write standard modern Serbian, the other being Gaj's Latin alphabet. Karadžić based his alphabet on the previous Slavonic-Serbian script, following the principle of "write as you speak and read as it is written", removing obsolete letters and letters representing iotified vowels, introducing from the Latin alphabet instead, and adding several consonant letters for sounds specific to Serbian phonology. During the same period, linguists led by Ljudevit Gaj adapted the Latin alphabet, in use in western South Slavic areas, using the same principles. As a result of this joint effort, Serbian Cyrillic and Gaj's Latin alphabets for Serbian-Croatian have a complete one-to-one congruence, with the Latin digraphs Lj, Nj, and Dž counting as single letters. Karadžić's Cyril ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belarusian Alphabet
The Belarusian alphabet is based on the Cyrillic script and is derived from the alphabet of Old Church Slavonic. It has existed in its modern form since 1918 and has 32 letters. See also Belarusian Latin alphabet and Belarusian Arabic alphabet. Letters Details Officially, the represents both and , but the latter occurs only in borrowings and mimesis. The is used by some for the latter sound but, with the exception of Taraškievica, has not been standard. A followed by or may denote either two distinct respective sounds (in some prefix-root combinations: пад-земны, ад-жыць) or the Belarusian affricates and (for example, падзея, джала). In some representations of the alphabet, the affricates are included in parentheses after the letter to emphasize their special status: . is not a distinct phoneme but the neutralization of /v/ and /l/ when there is no following vowel, like before a consonant or at the end of a word. Palatalization of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgarian Alphabet
The Bulgarian Cyrillic alphabet is used to write the Bulgarian language. The Cyrillic alphabet was originally developed in the First Bulgarian Empire during the 9th – 10th century AD at the Preslav Literary School. It has been used in Bulgaria (with modifications and exclusion of certain archaic letters via spelling reforms) continuously since then, superseding the previously used Glagolitic alphabet, which was also invented and used there before the Cyrillic script overtook its use as a written script for the Bulgarian language. The Cyrillic alphabet was used in the then much bigger territory of Bulgaria (including most of today's Serbia), North Macedonia, Kosovo, Albania, Northern Greece (Macedonia region), Romania and Moldova, officially from 893. It was also transferred from Bulgaria and adopted by the East Slavic languages in Kievan Rus' and evolved into the Belarusian, Russian and Ukrainian alphabets and the alphabets of many other Slavic (and later non-Slavic) langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phi (letter)
Phi (; uppercase Φ, lowercase φ or ϕ; grc, ϕεῖ ''pheî'' ; Modern Greek: ''fi'' ) is the 21st letter of the Greek alphabet. In Archaic and Classical Greek (c. 9th century BC to 4th century BC), it represented an aspirated voiceless bilabial plosive (), which was the origin of its usual romanization as . During the later part of Classical Antiquity, in Koine Greek (c. 4th century BC to 4th century AD), its pronunciation shifted to that of a voiceless bilabial fricative (), and by the Byzantine Greek period (c. 4th century AD to 15th century AD) it developed its modern pronunciation as a voiceless labiodental fricative (). The romanization of the Modern Greek phoneme is therefore usually . It may be that phi originated as the letter qoppa (Ϙ, ϙ), and initially represented the sound before shifting to Classical Greek . In traditional Greek numerals, phi has a value of 500 () or 500,000 (). The Cyrillic letter Ef (Ф, ф) descends from phi. As with other Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Cyrillic Alphabet
The Early Cyrillic alphabet, also called classical Cyrillic or paleo-Cyrillic, is a writing system that was developed in the First Bulgarian Empire during the late 9th century on the basis of the Greek alphabet for the Slavic people living near the Byzantine Empire in South East and Central Europe. It was used by Slavic peoples in South East, Central and Eastern Europe. It was developed in the Preslav Literary School in the capital city of the First Bulgarian Empire in order to write the Old Church Slavonic language. The modern Cyrillic script is still used primarily for some Slavic languages (such as Bulgarian, Macedonian, Serbian, Russian and Ukrainian), Kazakhstanand for East European and Asian languages that have experienced a great amount of Russian cultural influence. Among some of the traditionally culturally influential countries using Cyrillic script are Bulgaria, Russia, Serbia and Ukraine. Set А Б В Г Д Є Ж З И І К Л М Н О П Р С Т Ꙋ Ф ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Code Page 866
Code page 866 (CCSID 866) (CP 866, "DOS Cyrillic Russian") is a code page used under DOS and OS/2 in Russia to write Cyrillic script. It is based on the "alternative code page" (russian: Альтернативная кодировка) developed in 1984 in IHNA AS USSR and published in 1986 by a research group at the Academy of Science of the USSR. Брябрин В. М., Ландау И. Я., Неменман М. ЕО системе кодирования для персональных ЭВМ// Микропроцессорные средства и системы. — 1986. — № 4. — С. 61–64. The code page was widely used during the DOS era because it preserves all of the pseudographic symbols of code page 437 (unlike the " Main code page" or Code page 855) and maintains alphabetic order (although non-contiguously) of Cyrillic letters (unlike KOI8-R). Initially, this encoding was only available in the Russian version of MS-DOS 4.01 (1990) and since MS-DOS 6.22 in any l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fili (Moscow)
Fili (russian: Фили́) is a former suburban village, now a neighborhood in the western section of Moscow, Russia, notable for the events of September 1812, following the Battle of Borodino. The village was located between the Moskva River and Poklonnaya Hill, near the present-day Fili station of Moscow Metro and the extant Church of the Intercession at Fili. The territory is administered by Filyovsky park District (another related territory, Fili-Davydkovo District, lies southwest of historical Fili). History The first mention of Fili is dated 1627. From 1689, Fili, Kuntsevo, and adjacent settlements were owned by Lev Naryshkin, brother of tsaritsa Natalia Naryshkina. By 1694, he completed the Intercession Church, with donations by Peter I; its style is now known as Naryshkin Baroque. Naryshkin also established a new Fili village, closer to present-day Kutuzovsky Prospekt; the old Fili was remodelled into his personal estate. After the Battle of Borodino (September 7 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO-8859-5
ISO/IEC 8859-5:1999, ''Information technology — 8-bit single-byte coded graphic character sets — Part 5: Latin/Cyrillic alphabet'', is part of the ISO/IEC 8859 series of ASCII-based standard character encodings, first edition published in 1988. It is informally referred to as Latin/Cyrillic. It was designed to cover languages using a Cyrillic alphabet such as Bulgarian, Belarusian, Russian, Serbian and Macedonian but was never widely used. It would also have been usable for Ukrainian in the Soviet Union from 1933 to 1990, but it is missing the Ukrainian letter ''ge'', ґ, which is required in Ukrainian orthography before and since, and during that period outside Soviet Ukraine. As a result, IBM created Code page 1124. ISO-8859-5 is the IANA preferred charset name for this standard when supplemented with the C0 and C1 control codes from ISO/IEC 6429. The 8-bit encodings KOI8-R and KOI8-U, CP866, and also Windows-1251 are far more commonly used. In contrast to Windows-1252 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |