|
ĽAta
Ata is a depopulated island in the far southern end of the Tonga archipelago, situated approximately south-southwest of Tongatapu. It is distinct from AtńĀ, an uninhabited, low coral island in the string of small atolls along the Piha passage along the north side of Tongatapu. An unrelated traditional chiefly title from Kolovai is "Ata". Although superficially spelled in similar ways, Ata means ''reflection'' in Tongan; Ata means ''dawn'' and is the title of a chief; and AtńĀ means more room or expanding. Geography Most of Ata's land is a high plateau above sea level, with steep cliffs and rocky beaches ringing the shoreline of the entire island. There are three minor peaks: two on the west side and one on the east side of the island, ranging in elevation from (eastern) to (western). It has a total land area of approximately . Although it was apparently formed by volcanic action, no record of volcanic activity exists. The anchorage for Ata is on the west side of the isla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackbirding
Blackbirding was the trade in indentured labourers from the Pacific in the 19th and early 20th centuries. It is often described as a form of slavery, despite the British Slavery Abolition Act 1833 banning slavery throughout the British Empire, including Australia. The trade frequently relied on coercion, deception, and kidnapping to transport tens of thousands of indigenous people from islands in the Pacific Ocean to Australia and other European colonies, often to work on plantations in conditions similar to the Atlantic slave trade. These blackbirded people, known as Kanaka (Pacific Island worker), Kanakas or South Sea Islanders, were taken from places such as Papua New Guinea, the Solomon Islands, Vanuatu, Niue, Easter Island, the Gilbert Islands, Tuvalu and the islands of the Bismarck Archipelago, amongst others. The owners, captains, and crews of the ships involved in the acquisition of these labourers were termed ''blackbirders''. Blackbirding ships began operations in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
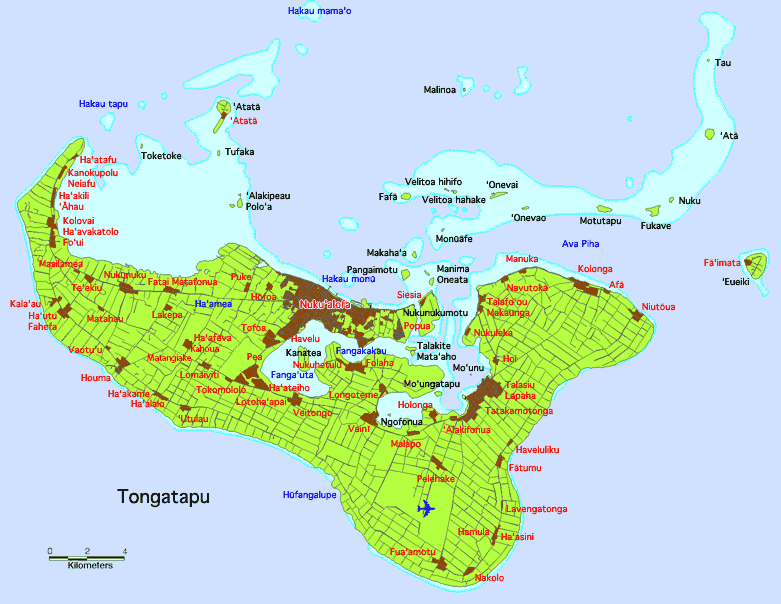
Tongatapu
Tongatapu is the main island of Tonga and the site of its capital, Nuku Ľalofa, Nukualofa. It is located in Tonga's southern island group, to which it gives its name, and is the country's most populous island, with 74,611 residents (2016), 70.5% of the national population, on . Tongatapu is Tonga's centre of government and the seat of its monarchy. Tongatapu has experienced more rapid economic development than the other islands of Tonga, and has thus attracted many internal migrants from them. Geography The island is (or including neighbouring islands) and rather flat, as it is built of coral limestone. The island is covered with thick fertile soil consisting of volcanic ash from neighbouring volcanoes. At the steep coast of the south, heights reach an average of , and maximum , gradually decreasing towards the north. North of the island are many small isolated islands and coral reefs which extend up to from Tongatapu's shores. The almost completely closed Fanga'uta and Fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast
The breasts are two prominences located on the upper ventral region of the torso among humans and other primates. Both sexes develop breasts from the same embryology, embryological tissues. The relative size and development of the breasts is a major secondary sex distinction between females and males. There is also considerable Bra size, variation in size between individuals. Permanent Breast development, breast growth during puberty is caused by estrogens in conjunction with the growth hormone. Female humans are the only mammals that permanently develop breasts at puberty; all other mammals develop their mammary tissue during the latter period of pregnancy. In females, the breast serves as the mammary gland, which produces and secretes milk to feed infants. Subcutaneous fat covers and envelops a network of lactiferous duct, ducts that converge on the nipple, and these tissue (biology), tissues give the breast its distinct size and globular shape. At the ends of the ducts are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lau Islands
The Lau Islands (also called the Lau Group, the Eastern Group, the Eastern Archipelago) of Fiji are situated in the southern Pacific Ocean, just east of the Koro Sea. Of this chain of about sixty islands and islets, about thirty are inhabited. The Lau Group covers a land area of 188 square miles (487 square km), and had a population of 10,683 at the most recent census in 2007. While most of the northern Lau Group are high islands of volcanic origin, those of the south are mostly carbonate low islands. Administratively the islands belong to Lau Province. History The United Kingdom, British explorer James Cook reached Vatoa in 1774. By the time of the discovery of the Ono Group in 1820, the Lau archipelago was the most mapped area of Fiji. Political unity came late to the Lau Islands. Historically, they comprised three territories: the Northern Lau Islands, the Southern Lau Islands, and the Moala Islands. Around 1855, the renegade Tongan prince Enele Ma'afu with the help ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Winslow Gifford
Edward Winslow Gifford (August 14, 1887 ‚Äď May 16, 1959) devoted his life to studying California Indian ethnography as a professor of anthropology and director of the Museum of Anthropology at the University of California, Berkeley. Gifford was born in Oakland, California. After graduating high school, he became an assistant curator of ornithology at the California Academy of Sciences. He never attended college. He joined the University of California's Museum of Anthropology in 1912 as an assistant curator. In the 1920s he was sent to Tonga with William C. McKern who was also from the University of California. With the botanist Arthur J. Eames from Harvard University Harvard University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the History of the Puritans in North America, Puritan clergyma ... they made up one of the four teams of the Bayard Dominick Exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otago Daily Times
The ''Otago Daily Times'' (''ODT'') is a newspaper published by Allied Press Ltd in Dunedin, New Zealand. The ''ODT'' is one of the country's four main daily newspapers, serving the southern South Island with a circulation of around 26,000 and a combined print and digital annual audience of 304,000. Founded in 1861 it is New Zealand's oldest surviving daily newspaper ‚Äď Christchurch's '' The Press'', six months older, was a weekly paper until March 1863. Its motto is "Optima Durant" or "Quality Endures". History Founding The ''ODT'' was founded by William H. Cutten and Julius (later Sir Julius) Vogel during the boom following the discovery of gold at the Tuapeka, the first of the Otago goldrushes. Co-founder Vogel had learnt the newspaper trade while working as a goldfields correspondent, journalist and editor in Victoria prior to immigrating to New Zealand. Vogel had arrived in Otago in early October 1861 at the age of 26 and soon took up employment at the ''Otago Colonis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chincha Islands
The Chincha Islands () are a group of three small islands off the southwest coast of Peru, to which they belong, near the town of Pisco. Since pre-Incan times they were of interest for their extensive guano deposits, but the supplies were mostly exhausted by 1874. Geography The largest of the islands, ''Isla Chincha Norte'' (English:North Chincha Island), is long and up to wide, and rises to a height of . ''Isla Chincha Centro'' (English:Center Chincha Island) is almost the same size as its neighbour to the north, while ''Isla Chincha Sur'' (English:South Chincha Island) is half the size of its neighbours. The islands are mostly granite, and bordered with cliffs on all sides, upon which great numbers of seabirds nest. History The Chincha Islands were once the residence of the Chincha people, but only a few remains are to be found today. Peru began the export of guano in 1840. Spain, which did not recognize Peru's independence until 1879 and desired the guano profits, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guano
Guano (Spanish from ) is the accumulated excrement of seabirds or bats. Guano is a highly effective fertiliser due to the high content of nitrogen, phosphate, and potassium, all key nutrients essential for plant growth. Guano was also, to a lesser extent, sought for the production of gunpowder and other explosive materials. The 19th-century seabird guano trade played a pivotal role in the development of modern Intensive farming, input-intensive farming. The demand for guano spurred the human colonisation of remote bird islands in many parts of the world. Unsustainable seabird guano mining processes can result in permanent habitat destruction and the loss of millions of seabirds. Bat guano is found in caves throughout the world. Many cave ecosystems are wholly dependent on bats to provide nutrients via their guano which supports bacteria, Fungus, fungi, invertebrates, and vertebrates. The loss of bats from a cave can result in the extinction of species that rely on their guano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southland Times
''The Southland Times'' is the regional daily paper for Southland Region, Southland, including Invercargill, and neighbouring parts of Otago, in New Zealand. It is now owned by media business Stuff (company), Stuff Ltd, formerly the New Zealand division of Fairfax Media. History ''The Southland Times'' was first established in 1862. The first edition was published on 12 November 1862 under the title of ''Invercargill Times''. The three founders were Gerard George Fitzgerald, John T. Downes, and Charles Reynolds. The name changed to ''The Southland Times'' in June 1864. Initially, it was published two or three times a week until it became a daily paper in 1875. From 1869 until its purchase by the INL (Independent Newspapers, Independent Newspapers Limited), it was owned by the Gilmour family. Robert Gilmour became a part owner in 1869‚Äď70, and then in 1879 became the sole owner of the paper. In 1972, digital computers and software, phototypesetters, and a Japanese APR photop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles St Julian
Charles James Herbert de Courcy St Julian (10 May 1819 ‚Äď 26 November 1874) was a journalist, newspaper owner-editor and the first Chief Justice of Fiji. St Julian's obituary records that he was born in France but other sources suggest London in 1818. He claimed to be the son of Thomas St Julian, French army officer, and his wife Marian, ''n√©e'' Blackwell. However, the Australian academic, Marion Diamond, in her biography of St Julian, claims that he deliberately obscured his origins and that it is likely that his real name was Charles Trout and that his initial training was as a wood and ivory carver. St Julian emigrated to Adelaide in 1837, proceeding in 1839 to Sydney, where he wrote for '' The Australasian Chronicle'', and subsequently for the '' Commercial Journal and Advertiser''. In 1843 he joined the staff of ''The Sydney Morning Herald'', which he left four years later for '' The Sydney Chronicle'', afterwards known as the ''Free Press''. In 1849 he rejoined ''The Syd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |