|
Bar (diacritic)
A bar or stroke is a modification consisting of a line drawn through a grapheme. It may be used as a diacritic to derive new letters from old ones, or simply as an addition to make a grapheme more distinct from others. It can take the form of a vertical bar, slash, or crossbar. A stroke is sometimes drawn through the numerals 7 (horizontal overbar) and 0 (overstruck foreslash), to make them more distinguishable from the number 1 and the letter O, respectively. (In some typefaces, one or other or both of these characters are designed in these styles; they are not produced by overstrike or by combining diacritic. The normal way in most of Europe to write the number seven is with a bar. ) In medieval English scribal abbreviations, a stroke or bar was used to indicate abbreviation. For example, , the pound sign, is a stylised form of the letter (the letter with a cross bar). For the specific usages of various letters with bars and strokes, see their individual articles. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jarai Language
Jarai (; , , , , , , or ; , ) is a Malayo-Polynesian language spoken by the Jarai people of Vietnam and Cambodia. The speakers of Jarai number approximately , not including other possible Jarai communities in countries other than Vietnam and Cambodia such as United States of America. They are the largest of the upland ethnic groups of Vietnam's Central Highlands known as Degar or Montagnards, and 25 per cent of the population in the Cambodian province of Ratanakiri. The language is in the Chamic subgroup of the Malayo-Polynesian languages, and is thus related to the Cham language of central Vietnam. A number of Jarai also live in the United States, having resettled there following the Vietnam War. Classification The Jarai language belongs to Chamic branch of the Malayo-Polynesian languages. Although often classified as a Mon-Khmer language until the 20th century, the affiliation of Jarai to the Chamic sister languages Cham and Rade, and a wider connection to Malay w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kiowa Language
Kiowa , in the language itself (also rendered , "language of the Kiowa"), is a Tanoan language spoken by the Kiowa people, primarily in Caddo, Kiowa, and Comanche counties. The Kiowa tribal center is located in Carnegie. Like most North American indigenous languages, Kiowa is an endangered language. Origins Although Kiowa is most closely related to the other Tanoan languages of the Pueblos, the earliest historic location of its speakers is western Montana around 1700. Prior to the historic record, oral histories, archaeology, and linguistics suggest that pre-Kiowa was the northernmost dialect of Proto-Kiowa-Tanoan, spoken at Late Basketmaker II Era sites. Around AD 450, they migrated northward through the territory of the Ancestral Puebloans and Great Basin, occupying the eastern Fremont culture region of the Colorado Plateau until sometime before 1300. Speakers then drifted northward to the northwestern Plains, arriving no later than the mid-16th century in the Yel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rade Language
Rade (Rhade; Rade: ; or ) is an Austronesian language of southern Vietnam. There may be some speakers in Cambodia. It is a member of the Chamic subgroup, and is closely related to the Cham language of central Vietnam. Dialects Đoàn Văn Phúc (1998:24) lists nine dialects of Rade. They are spoken mostly in Đắk Lắk Province in the Central Highlands region of Vietnam. *Kpă: spoken throughout Buôn Ma Thuột *Krung: spoken in Ea H'leo and Krông Năng; some Krung also live among the Jarai in Gia Lai Province *Adham: spoken in Krông Buk, Krông Năng, and Ea H'leo *Ktul: spoken in Krông Bông and the southern part of Krông Pắk *Drao (Kơdrao): spoken in M'Đrăk (in the townships of Krông Jing, Cư M'Ta, and Ea Trang) *Blô: spoken in M'Đrăk (small population) *Êpan: spoken in M'Đrăk (small population) *Mdhur: spoken in Ea Kar and M'Đrăk; also in Gia Lai Province and Phu Yen Province *Bih: spoken in Krông Ana and in the southern part of Bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Latin Script
The Latin script, also known as the Roman script, is a writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greek city of Cumae in Magna Graecia. The Greek alphabet was altered by the Etruscan civilization, Etruscans, and subsequently their alphabet was altered by the Ancient Romans. Several Latin-script alphabets exist, which differ in graphemes, collation and phonetic values from the classical Latin alphabet. The Latin script is the basis of the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA), and the 26 most widespread letters are the letters contained in the ISO basic Latin alphabet, which are the same letters as the English alphabet. Latin script is the basis for the largest number of alphabets of any writing system and is the List of writing systems by adoption, most widely adopted writing system in the world. Latin script is used as the standard method of writing the languages of Western and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Latin Alphabet
The Latin alphabet, also known as the Roman alphabet, is the collection of letters originally used by the Ancient Rome, ancient Romans to write the Latin language. Largely unaltered except several letters splitting—i.e. from , and from —additions such as , and extensions such as letters with diacritics, it forms the Latin script that is used to write most languages of modern Languages of Europe, Europe, languages of Africa, Africa, languages of the Americas, the Americas, and Languages of Oceania, Oceania. Its basic modern inventory is standardized as the ISO basic Latin alphabet. Etymology The term ''Latin alphabet'' may refer to either the alphabet used to write Latin (as described in this article) or other alphabets based on the Latin script, which is the basic set of letters common to the various alphabets descended from the classical Latin alphabet, such as the English alphabet. These Latin-script alphabets may discard letters, like the Rotokas alphabet, or add new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
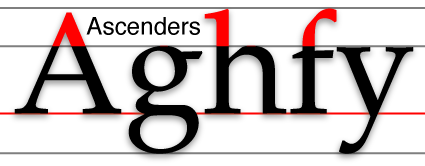
Ascender (typography)
In typography and handwriting, an ascender is the portion of a Lower case, minuscule grapheme, letter in a Latin-derived alphabet that extends above the mean line of a typeface, font. That is, the part of a lower-case letter that is taller than the font's x-height. Ascenders, together with descenders, increase the recognizability of words. For this reason, many situations that require high legibility such as road signs avoid using solely capital letters (i.e. all-caps). Studies made at the start of the construction of the British motorway network concluded that words with mixed-case letters were much easier to read than "all-caps" and a special font was designed for motorway signs. These then became universal across the UK. See Road signs in the United Kingdom. In many fonts intended for body text, such as Bembo and Garamond, ascenders rise above the cap height of the capital letters. References {{Typography terms [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Phonetic Symbol Guide
The ''Phonetic Symbol Guide'' is a book by Geoffrey Pullum and William Ladusaw that explains the histories and uses of the symbols of various phonetic transcription conventions. It was published in 1986, with a second edition in 1996, by the University of Chicago Press. Symbols include letters and diacritics of the International Phonetic Alphabet and Americanist phonetic notation, though not of the Uralic Phonetic Alphabet. The ''Guide'' was consulted by the International Phonetic Association when they established names and numerical codes for the International Phonetic Alphabet and was the basis for the characters of the TIPA (software), TIPA set of phonetic fonts. List of symbols The symbols included in the 2nd edition of the ''Guide'' are as follows. A number were adopted into Unicode 14 and 15 and have been available in SIL fonts since February 2023. Those not found in Unicode are marked with an asterisk. :wikt:a, a wikt:ȧ, ȧ wikt:ä, ä wikt:ᶏ, ᶏ wikt:ɐ, ɐ wikt:ɑ, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Phonetic Transcription
Phonetic transcription (also known as Phonetic script or Phonetic notation) is the visual representation of speech sounds (or ''phonetics'') by means of symbols. The most common type of phonetic transcription uses a phonetic alphabet, such as the International Phonetic Alphabet. Versus orthography The pronunciation of words in all languages changes over time. However, their written forms (orthography) are often not modified to take account of such changes, and do not accurately represent the pronunciation. Words borrowed from other languages may retain the spelling from the original language, which may have a different system of correspondences between written symbols and speech sounds. Pronunciation can also vary greatly among dialects of a language. Standard orthography in some languages, such as English language, English and Classical Tibetan, Tibetan, is often irregular and makes it difficult to predict pronunciation from spelling. For example, the words ''bough'', ''tough' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Katu Language
Katu, or Low Katu, is a Katuic language of eastern Laos and central Vietnam. In Vietnam, it is spoken in Huế city, including in A Lưới district. According to the 2009 Vietnamese census, there are 61,588 Katu people The Katuic people (also Co Tu, Ca Tang; ; Katu language, Katu: ) are an ethnic group of about 102,551 who live in eastern Laos and central Vietnam. Numbered among the Katuic peoples, they speak a Mon-Khmer languages, Mon-Khmer language. Katuic la .... Tổng điều tra dân số và nhà ở Việt Nam năm 2009: Kết quả toàn bộ. Hà Nội, 6-2010. Tabl. 5, p. 134-225. Accessed 10/2/2011 Phonology Consonants * can also be heard as a preglottal affricate sound or glide . ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifteenth-most populous country. One of two communist states in Southeast Asia, Vietnam shares land borders with China to the north, and Laos and Cambodia to the west. It shares Maritime boundary, maritime borders with Thailand through the Gulf of Thailand, and the Philippines, Indonesia, and Malaysia through the South China Sea. Its capital is Hanoi and its largest city is Ho Chi Minh City. Vietnam was inhabited by the Paleolithic age, with states established in the first millennium BC on the Red River Delta in modern-day northern Vietnam. Before the Han dynasty's invasion, Vietnam was marked by a vibrant mix of religion, culture, and social norms. The Han dynasty annexed Northern and Central Vietnam, which were subs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |