|
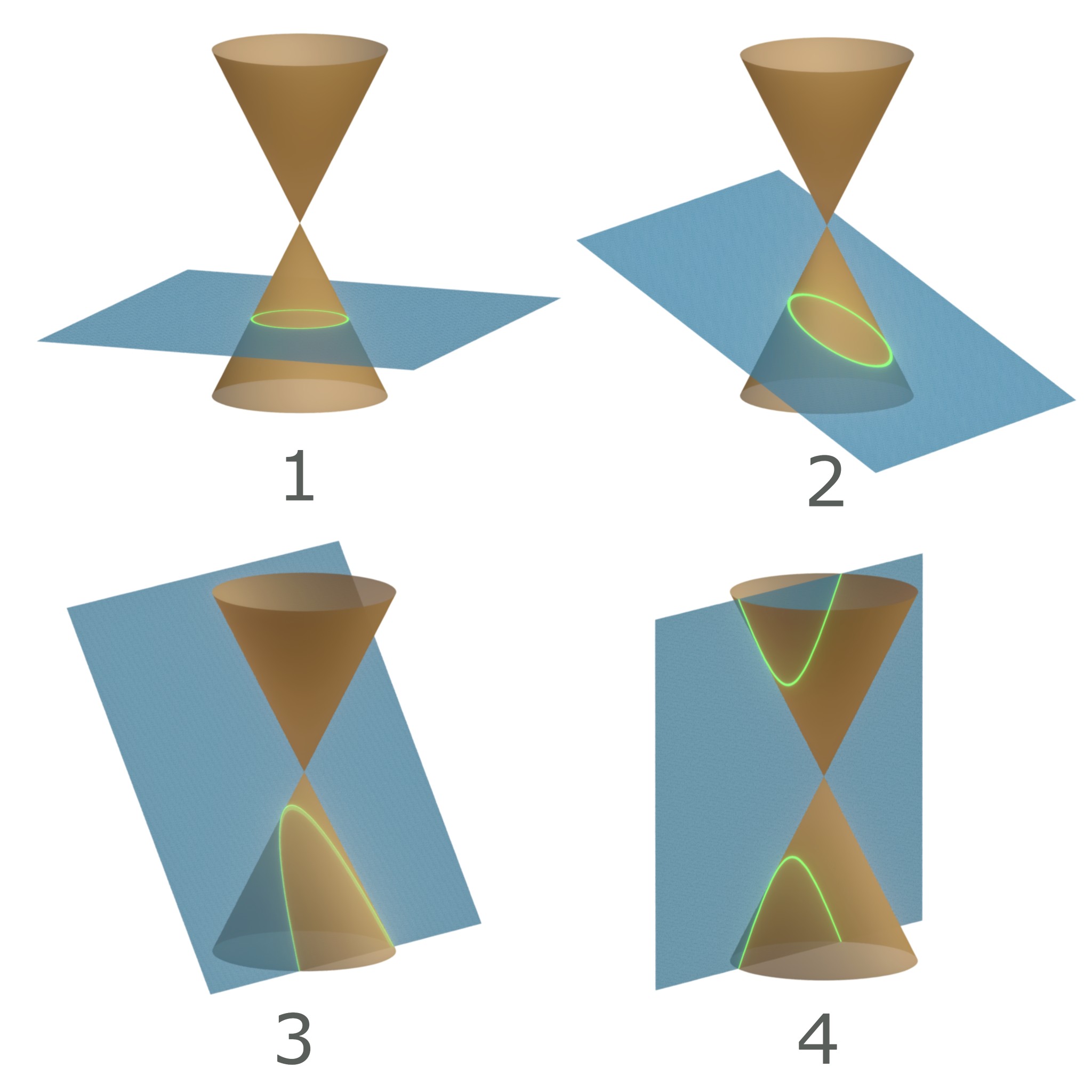
Conic Section
In mathematics, a conic section, quadratic curve or conic is a curve obtained as the intersection of the surface of a cone with a plane. The three types of conic section are the hyperbola, the parabola, and the ellipse; the circle is a special case of the ellipse, though historically it was sometimes called a fourth type. The ancient Greek mathematicians studied conic sections, culminating around 200 BC with Apollonius of Perga's systematic work on their properties. The conic sections in the Euclidean plane have various distinguishing properties, many of which can be used as alternative definitions. One such property defines a non-circular conic to be the set of those points whose distances to some particular point, called a ''focus'', and some particular line, called a ''directrix'', are in a fixed ratio, called the ''eccentricity''. The type of conic is determined by the value of the eccentricity. In analytic geometry, a conic may be defined as a plane algebraic curv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conic Sections
In mathematics, a conic section, quadratic curve or conic is a curve obtained as the intersection of the surface of a cone with a plane. The three types of conic section are the hyperbola, the parabola, and the ellipse; the circle is a special case of the ellipse, though historically it was sometimes called a fourth type. The ancient Greek mathematicians studied conic sections, culminating around 200 BC with Apollonius of Perga's systematic work on their properties. The conic sections in the Euclidean plane have various distinguishing properties, many of which can be used as alternative definitions. One such property defines a non-circular conic to be the set of those points whose distances to some particular point, called a '' focus'', and some particular line, called a ''directrix'', are in a fixed ratio, called the '' eccentricity''. The type of conic is determined by the value of the eccentricity. In analytic geometry, a conic may be defined as a plane algebraic curv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analytic Geometry
In classical mathematics, analytic geometry, also known as coordinate geometry or Cartesian geometry, is the study of geometry using a coordinate system. This contrasts with synthetic geometry. Analytic geometry is used in physics and engineering, and also in aviation, rocketry, space science, and spaceflight. It is the foundation of most modern fields of geometry, including algebraic, differential, discrete and computational geometry. Usually the Cartesian coordinate system is applied to manipulate equations for planes, straight lines, and circles, often in two and sometimes three dimensions. Geometrically, one studies the Euclidean plane (two dimensions) and Euclidean space. As taught in school books, analytic geometry can be explained more simply: it is concerned with defining and representing geometric shapes in a numerical way and extracting numerical information from shapes' numerical definitions and representations. That the algebra of the real numbers can be emplo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circle Of A Sphere
A circle of a sphere is a circle that lies on a sphere. Such a circle can be formed as the intersection of a sphere and a plane, or of two spheres. Circles of a sphere are the spherical geometry analogs of generalised circles in Euclidean space. A circle on a sphere whose plane passes through the center of the sphere is called a ''great circle'', analogous to a Euclidean straight line; otherwise it is a small circle, analogous to a Euclidean circle. Circles of a sphere have radius less than or equal to the sphere radius, with equality when the circle is a great circle. A circle of a sphere can also be characterized as the locus of points on the sphere at uniform distance from a given center point, or as a spherical curve of constant curvature. On the earth In the geographic coordinate system on a globe, the parallels of latitude are small circles, with the Equator the only great circle. By contrast, all meridians of longitude, paired with their opposite meridian in the other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |