|
Wilson Cycle
The Wilson Cycle is a model that describes the opening and closing of ocean basins and the subduction and divergence of tectonic plates during the assembly and disassembly of supercontinents. A classic example of the Wilson Cycle is the opening and closing of the Atlantic Ocean. It has been suggested that Wilson cycles on Earth started about 3 Ga in the Archean Eon. The Wilson Cycle model was a key development in the theory of plate tectonics during the Plate Tectonics Revolution. History The model is named after John Tuzo Wilson, in recognition of his iconic observation that the present-day Atlantic Ocean appears along a former suture zone and his development in a classic 1968 paper of what was later named the "Wilson cycle" in 1975 by Kevin C. A. Burke, a colleague and friend of Wilson.Wilson, R. W.; Houseman, G. A.; Buiter, S. J. H.; McCaffrey, K. J. W.; Doré, A. G. (2019). "Fifty years of the Wilson Cycle concept in plate tectonics: an overview". Geological Society, Lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock Cycle In Wilson Cycle
Rock most often refers to: * Rock (geology), a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals or mineraloids * Rock music, a genre of popular music Rock or Rocks may also refer to: Places United Kingdom * Rock, Caerphilly, a location in Wales * Rock, Cornwall, a village in England * Rock, County Tyrone, a village in Northern Ireland * Rock, Devon, a location in England * Rock, Neath Port Talbot, a location in Wales * Rock, Northumberland, a village in England * Rock, Somerset, a location in Wales * Rock, West Sussex, a hamlet in Washington, England * Rock, Worcestershire, a village and civil parish in England United States * Rock, Kansas, an unincorporated community * Rock, Michigan, an unincorporated community * Rock, West Virginia, an unincorporated community * Rock, Rock County, Wisconsin, a town in southern Wisconsin * Rock, Wood County, Wisconsin, a town in central Wisconsin Elsewhere * Corregidor, an island in the Philippines also known as "The Rock" * Jamaica, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 100 peaks exceeding in elevation lie in the Himalayas. By contrast, the highest peak outside Asia (Aconcagua, in the Andes) is tall. The Himalayas abut or cross five countries: Bhutan, India, Nepal, China, and Pakistan. The sovereignty of the range in the Kashmir region is disputed among India, Pakistan, and China. The Himalayan range is bordered on the northwest by the Karakoram and Hindu Kush ranges, on the north by the Tibetan Plateau, and on the south by the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Some of the world's major rivers, the Indus, the Ganges, and the Tsangpo– Brahmaputra, rise in the vicinity of the Himalayas, and their combined drainage basin is home to some 600 million people; 53 million people live in the Himalayas. The Himalayas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercontinent Cycle
The supercontinent cycle is the quasi-periodic aggregation and dispersal of Earth's continental crust. There are varying opinions as to whether the amount of continental crust is increasing, decreasing, or staying about the same, but it is agreed that the Earth's crust is constantly being reconfigured. One complete supercontinent cycle is said to take 300 to 500 million years. Continental collision makes fewer and larger continents while rifting makes more and smaller continents. Description The most recent supercontinent, Pangaea, formed about 300 million years ago (0.3 Ga). There are two different views on the history of earlier supercontinents. The first proposes a series of supercontinents: Vaalbara ( 3.6 to c. 2.8 billion years ago); Ur ( 3 billion years ago); Kenorland ( 2.7 to 2.1 billion years ago); Columbia ( 1.8 to 1.5 billion years ago); Rodinia ( 1.25 billion to 750 million years ago); and Pannotia ( 600 million years ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
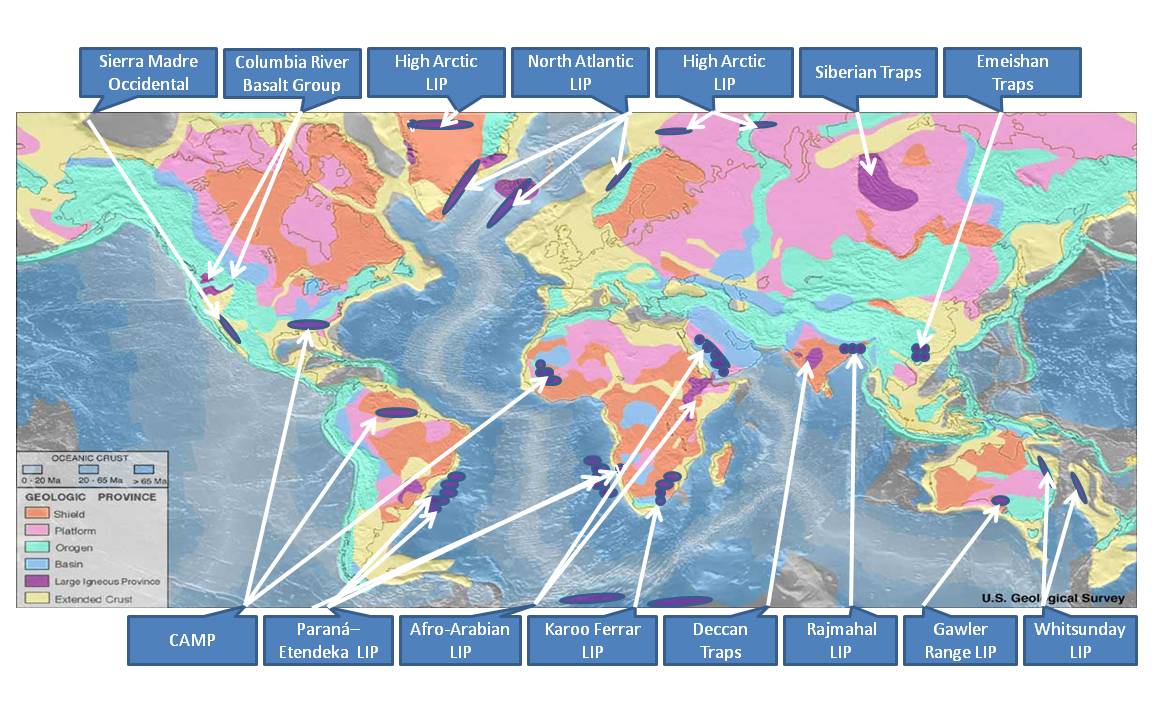
Large Igneous Province
A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including intrusive (sills, dikes) and extrusive (lava flows, tephra deposits), arising when magma travels through the crust towards the surface. The formation of LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with divergent plate tectonics. The formation of some of the LIPs in the past 500 million years coincide in time with mass extinctions and rapid climatic changes, which has led to numerous hypotheses about causal relationships. LIPs are fundamentally different from any other currently active volcanoes or volcanic systems. Definition In 1992 researchers first used the term ''large igneous province'' to describe very large accumulations—areas greater than 100,000 square kilometers (approximately the area of Iceland)—of mafic igneous rocks that were erupted or emplaced at depth within an extremely short geological time interval: a few million years or less. Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
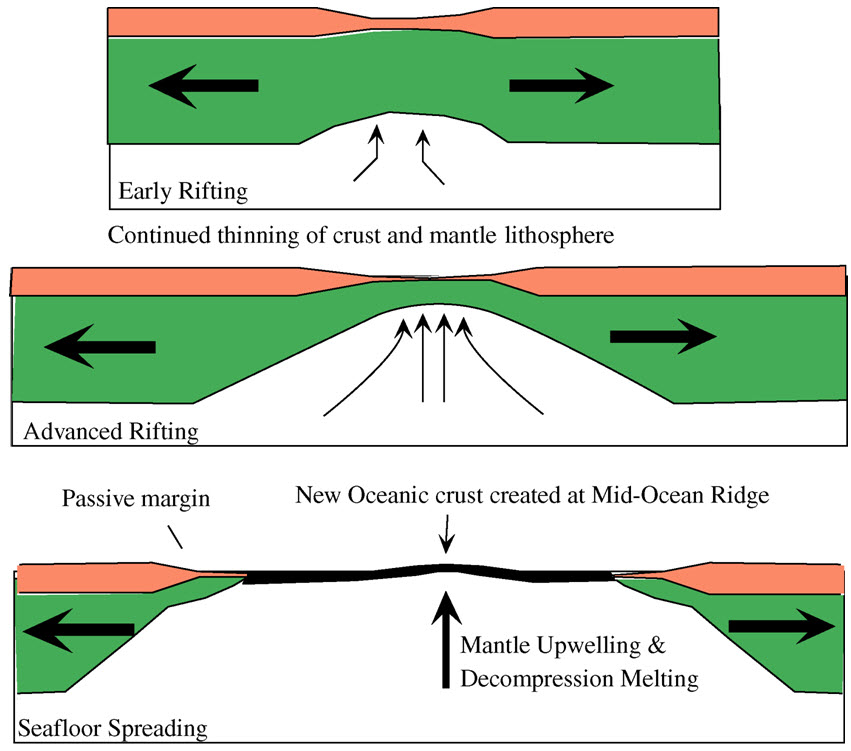
Passive Margin
A passive margin is the transition between oceanic and continental lithosphere that is not an active plate margin. A passive margin forms by sedimentation above an ancient rift, now marked by transitional lithosphere. Continental rifting creates new ocean basins. Eventually the continental rift forms a mid-ocean ridge and the locus of extension moves away from the continent-ocean boundary. The transition between the continental and oceanic lithosphere that was originally created by rifting is known as a passive margin. Global distribution Passive margins are found at every ocean and continent boundary that is not marked by a strike-slip fault or a subduction zone. Passive margins define the region around the Arctic Ocean, Atlantic Ocean, and western Indian Ocean, and define the entire coasts of Africa, Australia, Greenland, and the Indian Subcontinent. They are also found on the east coast of North America and South America, in Western Europe and most of Antarctica. Northea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Atlantic Igneous Province
The North Atlantic Igneous Province (NAIP) is a large igneous province in the North Atlantic, centered on Iceland. In the Paleogene, the province formed the Thulean Plateau, a large basaltic lava plain, which extended over at least in area and in volume. The plateau was broken up during the opening of the North Atlantic Ocean leaving remnants preserved in north Ireland, west Scotland, the Faroe Islands, northwest Iceland, east Greenland, western Norway and many of the islands located in the north eastern portion of the North Atlantic Ocean. The igneous province is the origin of the Giant's Causeway and Fingal's Cave. The province is also known as Brito–Arctic province (also known as the North Atlantic Tertiary Volcanic Province) and the portion of the province in the British Isles is also called the British Tertiary Volcanic Province or British Tertiary Igneous Province. Formation Isotopic dating indicates the most active magmatic phase of the NAIP was between and c. 54.5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congo Craton
The Congo Craton, covered by the Palaeozoic-to-recent Congo Basin, is an ancient Precambrian craton that with four others (the Kaapvaal, Zimbabwe, Tanzania, and West African cratons) makes up the modern continent of Africa. These cratons were formed between about 3.6 and 2.0 billion years ago and have been tectonically stable since that time. All of these cratons are bounded by younger fold belts formed between 2.0 billion and 300 million years ago. The Congo Craton occupies a large part of central southern Africa, extending from the Kasai region of the DRC into Sudan and Angola. It forms parts of the countries of Gabon, Cameroon, and the Central African Republic. A small portion extends into Zambia as well, where it is called the Bangweulu Block. Congo–São Francisco The Congo Craton and the São Francisco Craton are stable Archaean blocks that formed a coherent landmass until the opening of the South Atlantic Ocean during the break-up of Gondwana ( 2000–130 Ma). Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
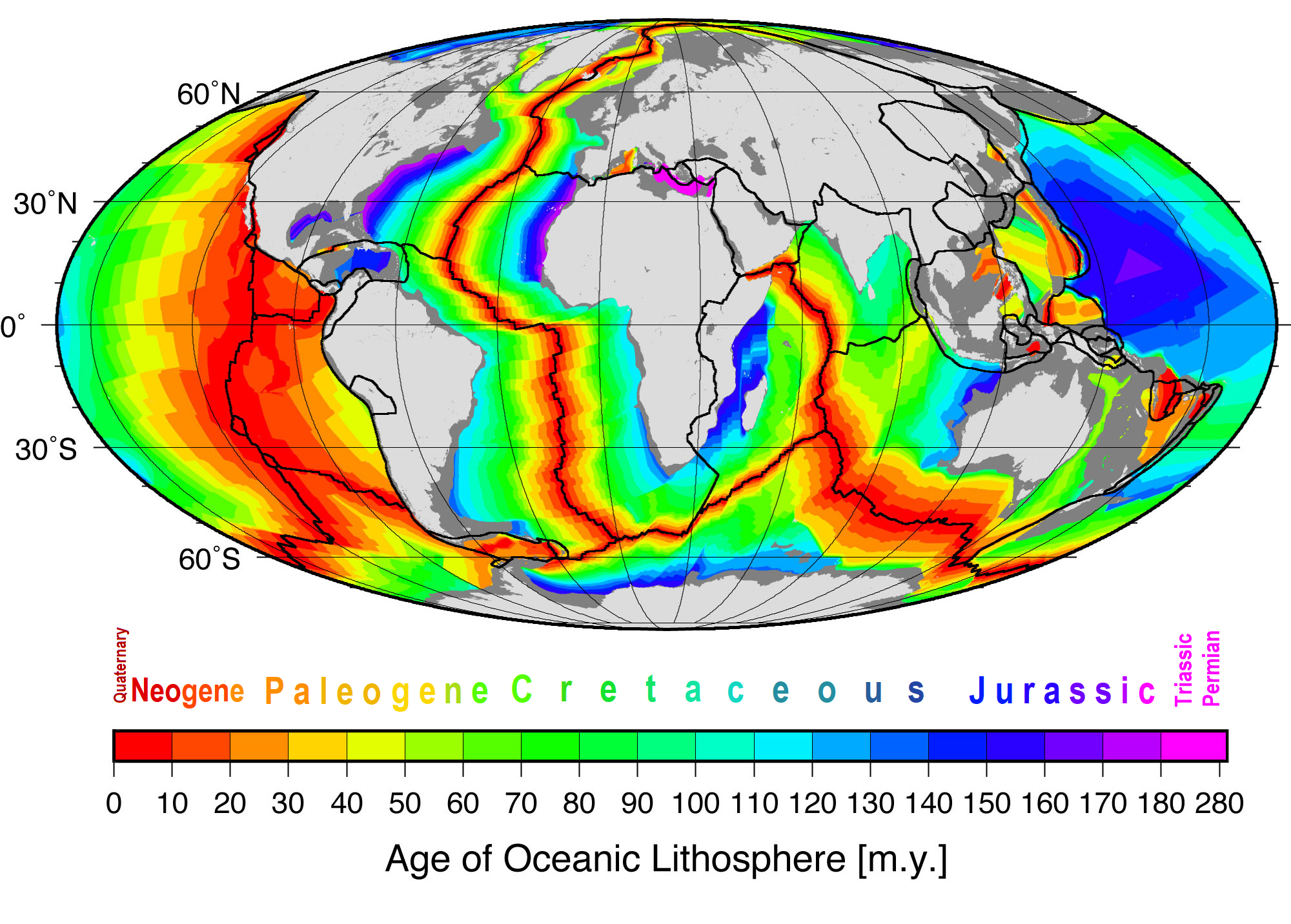
Seafloor Spreading
Seafloor spreading or Seafloor spread is a process that occurs at mid-ocean ridges, where new oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the ridge. History of study Earlier theories by Alfred Wegener and Alexander du Toit of continental drift postulated that continents in motion "plowed" through the fixed and immovable seafloor. The idea that the seafloor itself moves and also carries the continents with it as it spreads from a central rift axis was proposed by Harold Hammond Hess from Princeton University and Robert Dietz of the U.S. Naval Electronics Laboratory in San Diego in the 1960s. The phenomenon is known today as plate tectonics. In locations where two plates move apart, at mid-ocean ridges, new seafloor is continually formed during seafloor spreading. Significance Seafloor spreading helps explain continental drift in the theory of plate tectonics. When oceanic plates diverge, tensional stress causes fractures to occur in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheic Ocean
The Rheic Ocean was an ocean which separated two major palaeocontinents, Gondwana and Laurussia (Laurentia- Baltica-Avalonia). One of the principal oceans of the Palaeozoic, its sutures today stretch from Mexico to Turkey and its closure resulted in the assembly of the supercontinent Pangaea and the formation of the Variscan– Alleghenian– Ouachita orogenies. Etymology The ocean located between Gondwana and Laurentia in the Early Cambrian was named for Iapetus, in Greek mythology the father of Atlas (from which source the Atlantic Ocean ultimately gets its name), just as the Iapetus Ocean was the predecessor of the Atlantic Ocean. The ocean between Gondwana and Laurussia (Laurentia– Baltica–Avalonia) that existed from the Early Ordovician to the Early Carboniferous was named the Rheic Ocean after Rhea, sister of Iapetus. Geodynamic evolution At the beginning of the Paleozoic Era, about 540 million years ago, most of the continental mass on Earth was clustered aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pan-African Orogeny
The Pan-African orogeny was a series of major Neoproterozoic orogenic events which related to the formation of the supercontinents Gondwana and Pannotia about 600 million years ago. This orogeny is also known as the Pan-Gondwanan or Saldanian Orogeny. The Pan-African orogeny and the Grenville orogeny are the largest known systems of orogenies on Earth. The sum of the continental crust formed in the Pan-African orogeny and the Grenville orogeny makes the Neoproterozoic the period of Earth's history that has produced most continental crust. History and terminology The term ''Pan-African'' was coined by for a tectono-thermal event at about 500 Ma when a series of mobile belts in Africa formed between much older African cratons. At the time, other terms were used for similar orogenic events on other continents, i.e. '' Brasiliano'' in South America; ''Adelaidean'' in Australia; and ''Beardmore'' in Antarctica. Later, when plate tectonics became generally accepted, the term ''Pan-A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cenozoic
The Cenozoic ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configuration of continents. It is the latest of three geological eras since complex life evolved, preceded by the Mesozoic and Paleozoic. It started with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, when many species, including the non-avian dinosaurs, became extinct in an event attributed by most experts to the impact of a large asteroid or other celestial body, the Chicxulub impactor. The Cenozoic is also known as the Age of Mammals because the terrestrial animals that dominated both hemispheres were mammalsthe eutherians (placentals) in the northern hemisphere and the metatherians (marsupials, now mainly restricted to Australia) in the southern hemisphere. The extinction of many groups allowed mammals and birds to greatly diversify so tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Periods. It is characterized by the dominance of archosaurian reptiles, like the dinosaurs; an abundance of conifers and ferns; a hot greenhouse climate; and the tectonic break-up of Pangaea. The Mesozoic is the middle of the three eras since complex life evolved: the Paleozoic, the Mesozoic, and the Cenozoic. The era began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, the largest well-documented mass extinction in Earth's history, and ended with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, another mass extinction whose victims included the non-avian dinosaurs, pterosaurs, mosasaurs, and plesiosaurs. The Mesozoic was a time of significant tectonic, climatic, and evolutionary activity. The era witnessed the gradual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |