|
Gravity Probe B
Gravity Probe B (GP-B) was a satellite-based experiment to test two unverified predictions of general relativity: the geodetic effect and frame-dragging. This was to be accomplished by measuring, very precisely, tiny changes in the direction of spin of four gyroscopes contained in an Earth-orbiting satellite at of altitude, crossing directly over the poles. The satellite was launched on 20 April 2004 on a Delta II rocket. The spaceflight phase lasted until 2005; Its aim was to measure spacetime curvature near Earth, and thereby the stress–energy tensor (which is related to the distribution and the motion of matter in space) in and near Earth. This provided a test of general relativity, gravitomagnetism and related models. The principal investigator was Francis Everitt. Initial results confirmed the expected geodetic effect to an accuracy of about 1%. The expected frame-dragging effect was similar in magnitude to the current noise level (the noise being dominated by initially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyroscope
A gyroscope (from Ancient Greek γῦρος ''gŷros'', "round" and σκοπέω ''skopéō'', "to look") is a device used for measuring or maintaining orientation and angular velocity. It is a spinning wheel or disc in which the axis of rotation (spin axis) is free to assume any orientation by itself. When rotating, the orientation of this axis is unaffected by tilting or rotation of the mounting, according to the conservation of angular momentum. Gyroscopes based on other operating principles also exist, such as the microchip-packaged MEMS gyroscopes found in electronic devices (sometimes called gyrometers), solid-state ring lasers, fibre optic gyroscopes, and the extremely sensitive quantum gyroscope. Applications of gyroscopes include inertial navigation systems, such as in the Hubble Space Telescope, or inside the steel hull of a submerged submarine. Due to their precision, gyroscopes are also used in gyrotheodolites to maintain direction in tunnel mining. Gyroscope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frame-dragging
Frame-dragging is an effect on spacetime, predicted by Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity, that is due to non-static stationary distributions of mass–energy. A stationary field is one that is in a steady state, but the masses causing that field may be non-static — rotating, for instance. More generally, the subject that deals with the effects caused by mass–energy currents is known as gravitoelectromagnetism, which is analogous to the magnetism of classical electromagnetism. The first frame-dragging effect was derived in 1918, in the framework of general relativity, by the Austrian physicists Josef Lense and Hans Thirring, and is also known as the Lense–Thirring effect. They predicted that the rotation of a massive object would distort the spacetime metric, making the orbit of a nearby test particle precess. This does not happen in Newtonian mechanics for which the gravitational field of a body depends only on its mass, not on its rotation. The L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravity Probe B
Gravity Probe B (GP-B) was a satellite-based experiment to test two unverified predictions of general relativity: the geodetic effect and frame-dragging. This was to be accomplished by measuring, very precisely, tiny changes in the direction of spin of four gyroscopes contained in an Earth-orbiting satellite at of altitude, crossing directly over the poles. The satellite was launched on 20 April 2004 on a Delta II rocket. The spaceflight phase lasted until 2005; Its aim was to measure spacetime curvature near Earth, and thereby the stress–energy tensor (which is related to the distribution and the motion of matter in space) in and near Earth. This provided a test of general relativity, gravitomagnetism and related models. The principal investigator was Francis Everitt. Initial results confirmed the expected geodetic effect to an accuracy of about 1%. The expected frame-dragging effect was similar in magnitude to the current noise level (the noise being dominated by initially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program, aeronautics research, and outer space, space research. NASA was National Aeronautics and Space Act, established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo program, Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew Program, Commercial Crew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Review Letters
''Physical Review Letters'' (''PRL''), established in 1958, is a peer-reviewed, scientific journal that is published 52 times per year by the American Physical Society. As also confirmed by various measurement standards, which include the ''Journal Citation Reports'' impact factor and the journal ''h''-index proposed by Google Scholar, many physicists and other scientists consider ''Physical Review Letters'' to be one of the most prestigious journals in the field of physics. ''According to Google Scholar, PRL is the journal with the 9th journal h-index among all scientific journals'' ''PRL'' is published as a print journal, and is in electronic format, online and CD-ROM. Its focus is rapid dissemination of significant, or notable, results of fundamental research on all topics related to all fields of physics. This is accomplished by rapid publication of short reports, called "Letters". Papers are published and available electronically one article at a time. When published in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central European Journal Of Physics
''Open Physics'' is a peer-reviewed open access scientific journal covering all aspects of physics. It is published by De Gruyter and the editor-in-chief is Sally Seidel (University of New Mexico). Occasionally, the journal publishes special issues on a specific topic. History The journal was established in 2003 as the ''Central European Journal of Physics''. It was co-published by Versita and Springer Science+Business Media. The founding editor-in-chief was Janos Lendvai ( Eötvös Loránd University), who was succeeded in 2004 by Vladimir E. Zakharov (University of Arizona and Lebedev Physical Institute) and in 2011 by Feng. In 2014 the journal was moved to De Gruyter. It obtained its current name in 2015 and simultaneously became open access. Abstracting and indexing The journals is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planetary And Space Science
''Planetary and Space Science'' (P&SS), published 15 times per year, is a peer-reviewed scientific journal established in 1959. It publishes original research articles along with short communications (letters). The main topic is Solar System processes which encompasses multiple areas of the natural sciences. Numerical simulations of solar system processes are also conducted at ground-based facilities or on-board space platforms. The editor-in-chief is Maria Cristina De Sanctis (National Institute of Astrophysics, Roma, Italy). It is published by Elsevier. Scope Research that involves planetary and space sciences involves many disciplines, which is reflected by the scope of the journal. Basic science Celestial mechanics is part of these studies, as this science includes understanding the dynamic evolution of the Solar System, relativistic effects, among other areas of analysis and consideration. Cosmochemistry is also part of the published research in this journal. Cosmoche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Geodesy
The ''Journal of Geodesy'' is an academic journal about geodesy published by Springer on behalf of the International Association of Geodesy (IAG). It is the merger and continuation of ''Bulletin Géodésique'' and ''manuscripta geodaetica'' (both published 1976-1995). This journal has an impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 4.528 (2018). References External links Journal of Geodesy- Springer Earth and atmospheric sciences journals Academic journals associated with international learned and professional societies Springer Science+Business Media academic journals Geodesy {{geodesy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Astronomy (journal)
''New Astronomy'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering topics in astronomy and astrophysics. The journal was established in 1996 and is currently published by Elsevier. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in the following databases: *Current Contents/Physics, Chemical, & Earth Sciences * INSPEC * SCISEARCH *Science Citation Index *Scopus According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 1.325. References External links * Astronomy journals Elsevier academic journals English-language journals Publications established in 1996 {{astronomy-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2019 '' Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 42.778), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in autumn 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander Macmillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the journal; ''Nature'' redoubled its efforts in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
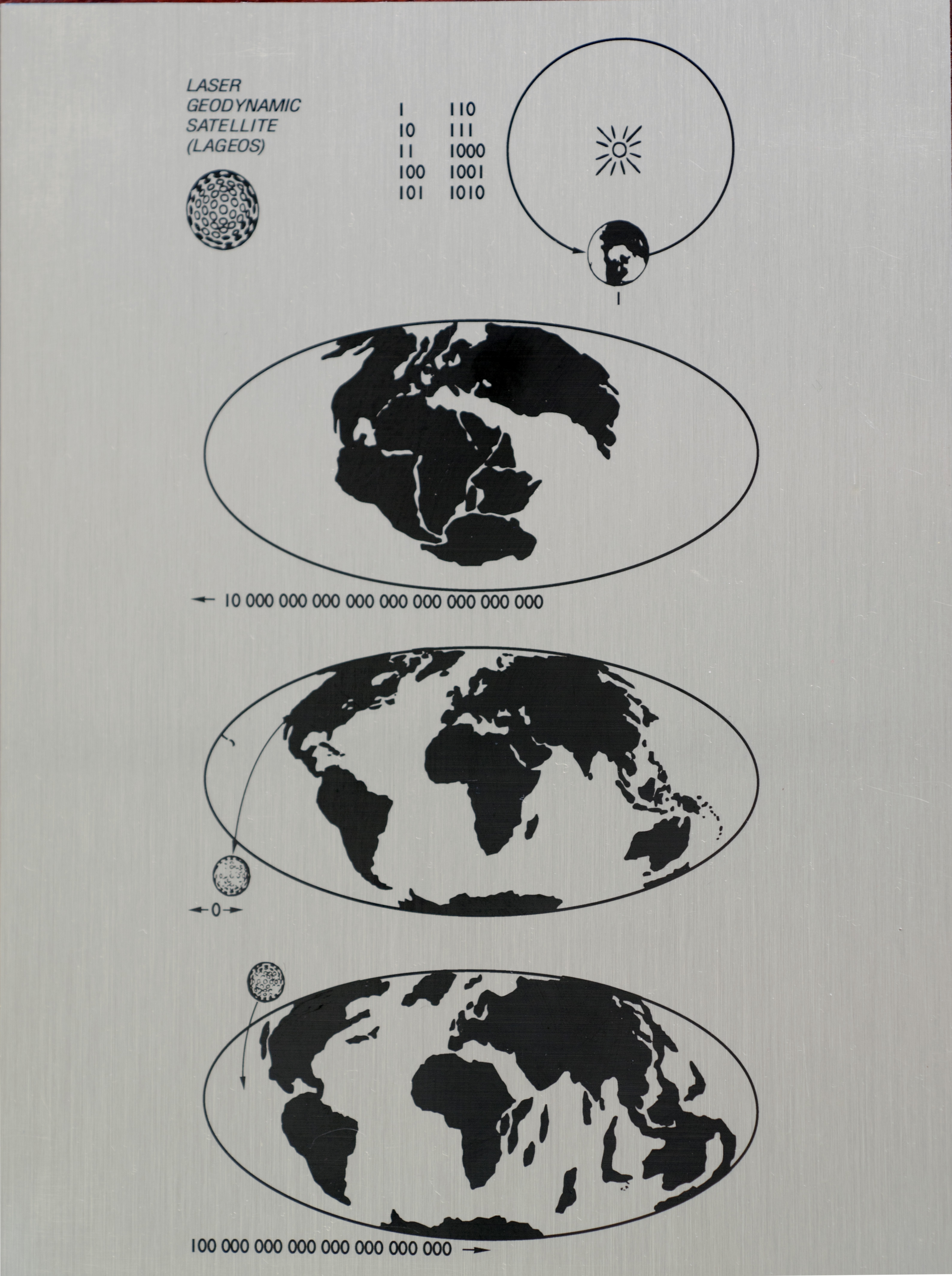
LAGEOS
LAGEOS, Laser Geodynamics Satellite or Laser Geometric Environmental Observation Survey, are a series of two scientific research satellites designed to provide an orbiting laser ranging benchmark for geodynamical studies of the Earth. Each satellite is a high-density passive laser reflector in a very stable medium Earth orbit (MEO). Function and operation The spacecraft are aluminum-covered brass spheres with diameters of and masses of , covered with 426 cube-corner retroreflectors, giving them the appearance of giant golf balls. Of these retroreflectors, 422 are made from fused silica glass while the remaining 4 are made from germanium to obtain measurements in the infrared for experimental studies of reflectivity and satellite orientation. They have no on-board sensors or electronics, and are not attitude-controlled. They orbit at an altitude of , well above low Earth orbit and well below geostationary orbit, at orbital inclinations of 109.8 and 52.6 degrees. Measurements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser-ranging
A laser rangefinder, also known as a laser telemeter, is a rangefinder that uses a laser beam to determine the distance to an object. The most common form of laser rangefinder operates on the time of flight principle by sending a laser pulse in a narrow beam towards the object and measuring the time taken by the pulse to be reflected off the target and returned to the sender. Due to the high speed of light, this technique is not appropriate for high precision sub-millimeter measurements, where triangulation and other techniques are often used. Pulse The pulse may be coded to reduce the chance that the rangefinder can be jammed. It is possible to use Doppler effect techniques to judge whether the object is moving towards or away from the rangefinder, and if so, how fast. Precision The precision of the instrument is determined by the rise or fall time of the laser pulse and the speed of the receiver. One that uses very sharp laser pulses and has a very fast detector can range ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.gif)