|
Esperanto Language
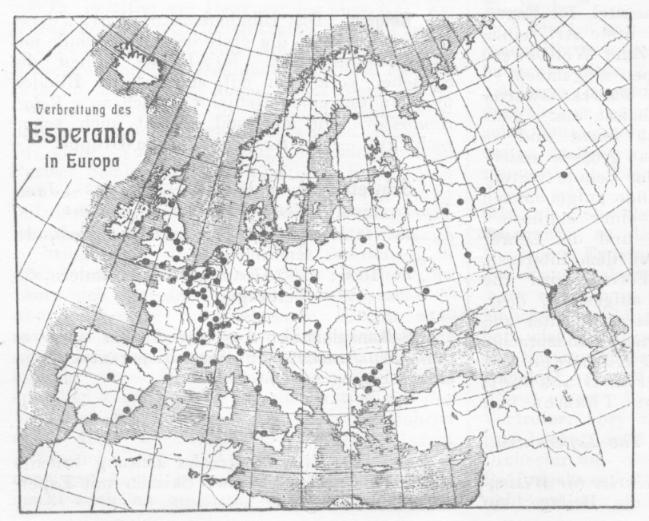
Esperanto ( or ) is the world's most widely spoken constructed international auxiliary language. Created by the Warsaw-based ophthalmologist L. L. Zamenhof in 1887, it was intended to be a universal second language for international communication, or "the international language" (). Zamenhof first described the language in '' Dr. Esperanto's International Language'' (), which he published under the pseudonym . Early adopters of the language liked the name ''Esperanto'' and soon used it to describe his language. The word translates into English as "one who hopes". Within the range of constructed languages, Esperanto occupies a middle ground between "naturalistic" (imitating existing natural languages) and ''a'priori'' (where features are not based on existing languages). Esperanto's vocabulary, syntax and semantics derive predominantly from languages of the Indo-European group. The vocabulary derives primarily from Romance languages, with substantial contributions from Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native Esperanto Speakers
Native Esperanto speakers ( Esperanto: ''denaskuloj'' or ''denaskaj esperantistoj'') are people who have acquired Esperanto as one of their native languages. As of 1996, there were 350 or so attested cases of families with native Esperanto speakers. Estimates from associations indicate that there were around 1,000 Esperanto-speaking families, involving perhaps 2,000 children in 2004. According to a 2019 synthesis of all the estimates made, they would be between several hundred and 2000, and would compose between <1% and 4.5% of the Esperanto community. In all known cases, speakers are natively bilingual, or multilingual, raised in both Esperanto and either the local national language or the native language of their parents. In all but a handful of cases, it was the father who used Esperanto with the child. In the majority of such families, the parents had the same native language, thoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmologist
Ophthalmology ( ) is a surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of eye disorders. An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a medical degree, a doctor specialising in ophthalmology must pursue additional postgraduate residency training specific to that field. This may include a one-year integrated internship that involves more general medical training in other fields such as internal medicine or general surgery. Following residency, additional specialty training (or fellowship) may be sought in a particular aspect of eye pathology. Ophthalmologists prescribe medications to treat eye diseases, implement laser therapy, and perform surgery when needed. Ophthalmologists provide both primary and specialty eye care - medical and surgical. Most ophthalmologists participate in academic research on eye diseases at some point in their training and many include research as p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unua Libro Ru 1st Ed
Unua, or Onua, is an Oceanic language spoken in south-east Malekula, Vanuatu Vanuatu ( or ; ), officially the Republic of Vanuatu (french: link=no, République de Vanuatu; bi, Ripablik blong Vanuatu), is an island country located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is east of no .... It is said to be a dialect of the same language, Unua-Pangkumu, as Rerep (Pangkumu). Phonology The following table lists the contrastive consonant sounds of Unua. There are 16 consonant phonemes for younger Unua speakers and an additional three contrastive velarized labial consonants for older speakers, shown below in parentheses. The following table lists the contrastive vowel sounds of Unua. Younger speakers have five vowel phonemes and older speakers have an additional three, shown in parentheses. Grammar Unua has SVO ordering. References Malekula languages Languages of Vanuatu {{SOceanic-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Google Translate
Google Translate is a multilingual neural machine translation service developed by Google to translate text, documents and websites from one language into another. It offers a website interface, a mobile app for Android and iOS, and an API that helps developers build browser extensions and software applications. As of , Google Translate supports languages at various levels, and , claimed over 500 million total users, with more than 100 billion words translated daily, after the company stated in May 2013 that it served over 200 million people daily. Launched in April 2006 as a statistical machine translation service, it used United Nations and European Parliament documents and transcripts to gather linguistic data. Rather than translating languages directly, it first translates text to English and then pivots to the target language in most of the language combinations it posits in its grid, with a few exceptions including Catalan-Spanish. During a translation, it looks fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amikumu
Amikumu ( ; ) is a cross-platform app for smartphones ( Android and iOS) which can be used to find people nearby who speak or learn the same languages as the user. The app was launched for Esperanto speakers on 22 April 2017 and for speakers of all languages during LangFest in Montreal on 25 August 2017. On 9 August 2018 Amikumu had members in more than 130 countries speaking 588 languages. Architecture The Android app is written in Java and Kotlin, the iOS app in Swift, and the server in Ruby on Rails Ruby on Rails (simplified as Rails) is a server-side web application framework written in Ruby under the MIT License. Rails is a model–view–controller (MVC) framework, providing default structures for a database, a web service, and we .... Kickstarter campaign Amikumu was funded in part using Kickstarter. The Kickstarter campaign, organized by Esperanto speakers Chuck Smith and Richard "Evildea" Delamore, launched on 18 October 2016. More than 3000 euros were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esperanto Wikipedia
The Esperanto Wikipedia ( eo, Vikipedio en Esperanto, or ) is the Esperanto version of Wikipedia, which was started on 11 May 2001, alongside the Basque Wikipedia. With over articles , it is the - largest Wikipedia as measured by the number of articles, and the largest Wikipedia in a constructed language. Origin and influence of the Esperanto Wikipedia Chuck Smith, an American Esperantist, is considered to be Esperanto Wikipedia's founder. The encyclopedia started off when he imported the 139 articles of the by Stefano Kalb, which took him three weeks following 15 November 2001. Later on, he undertook a journey to Europe with the goal of popularizing Wikipedia among the speakers of Esperanto in European countries. For instance, in November 2002 he gave a talk about Wikipedia at the 10th Conference on the Application of Esperanto in Science and Technology in Dobřichovice (Czech Republic). Esperanto speakers have also been involved in the founding of several other lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duolingo
Duolingo ( ) is an American educational technology company which produces learning apps and provides language certification. On its main app, users can practice vocabulary, grammar, pronunciation and listening skills using spaced repetition. Duolingo offers over 100 total courses across over 40 distinct languages; including a small variety of constructed languages. The company uses a freemium model with over 500 million registered users. Duolingo offers a premium service which eliminates advertising and offers more features. Duolingo also offers the Duolingo English Test certification program and a literacy app for children called Duolingo ABC, and the company released an elementary level math app called Duolingo Math currently exclusive to iOS. History The idea for Duolingo was initiated at the end of 2009 in Pittsburgh by Carnegie Mellon University professor Luis von Ahn and his post-graduate student Severin Hacker. Von Ahn had sold his second company, reCAPTCHA, to Google ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Language
A first language, native tongue, native language, mother tongue or L1 is the first language or dialect that a person has been exposed to from birth or within the critical period. In some countries, the term ''native language'' or ''mother tongue'' refers to the language or dialect of one's ethnic group rather than one's first language. The first language of a child is part of that child's personal, social and cultural identity. Another impact of the first language is that it brings about the reflection and learning of successful social patterns of acting and speaking. Research suggests that while a non-native speaker may develop fluency in a targeted language after about two years of immersion, it can take between five and seven years for that child to be on the same working level as their native speaking counterparts. On 17 November 1999, UNESCO designated 21 February as International Mother Language Day. Definitions One of the more widely accepted definitions of native sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agglutination
In linguistics, agglutination is a morphological process in which words are formed by stringing together morphemes, each of which corresponds to a single syntactic feature. Languages that use agglutination widely are called agglutinative languages. Turkish is an example of an agglutinative language. The Turkish word ("from your houses") consists of the morphemes ''ev-ler-iniz-den,'' literally translated morpheme-by-morpheme as ''house-plural-your(plural)-from''. Agglutinative languages are often contrasted with isolating languages, in which words are monomorphemic, and fusional languages, in which words can be complex, but morphemes may correspond to multiple features. Examples of agglutinative languages Although agglutination is characteristic of certain language families, this does not mean that when several languages in a certain geographic area are all agglutinative they are necessarily related phylogenetically. In the past, this assumption led linguists to propose the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-European Languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch, and Spanish, have expanded through colonialism in the modern period and are now spoken across several continents. The Indo-European family is divided into several branches or sub-families, of which there are eight groups with languages still alive today: Albanian, Armenian, Balto-Slavic, Celtic, Germanic, Hellenic, Indo-Iranian, and Italic; and another nine subdivisions that are now extinct. Today, the individual Indo-European languages with the most native speakers are English, Hindi–Urdu, Spanish, Bengali, French, Russian, Portuguese, German, and Punjabi, each with over 100 million native speakers; many others are small and in danger of extinction. In total, 46% of the world's population (3.2 billion people) speaks an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantics
Semantics (from grc, σημαντικός ''sēmantikós'', "significant") is the study of reference, meaning, or truth. The term can be used to refer to subfields of several distinct disciplines, including philosophy, linguistics and computer science. History In English, the study of meaning in language has been known by many names that involve the Ancient Greek word (''sema'', "sign, mark, token"). In 1690, a Greek rendering of the term ''semiotics'', the interpretation of signs and symbols, finds an early allusion in John Locke's ''An Essay Concerning Human Understanding'': The third Branch may be called [''simeiotikí'', "semiotics"], or the Doctrine of Signs, the most usual whereof being words, it is aptly enough termed also , Logick. In 1831, the term is suggested for the third branch of division of knowledge akin to Locke; the "signs of our knowledge". In 1857, the term '' semasiology'' (borrowed from German ''Semasiologie'') is attested in Josiah W. Gibb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syntax
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure ( constituency), agreement, the nature of crosslinguistic variation, and the relationship between form and meaning (semantics). There are numerous approaches to syntax that differ in their central assumptions and goals. Etymology The word ''syntax'' comes from Ancient Greek roots: "coordination", which consists of ''syn'', "together", and ''táxis'', "ordering". Topics The field of syntax contains a number of various topics that a syntactic theory is often designed to handle. The relation between the topics is treated differently in different theories, and some of them may not be considered to be distinct but instead to be derived from one another (i.e. word order can be seen as the result of movement rules derived from grammatical relations). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |